Dental Information and Tips from St. Jacobs Dental Care
Dental Crowns and Bridges vs Implants: Right Choice
February 22, 2026 / DENTISTRY
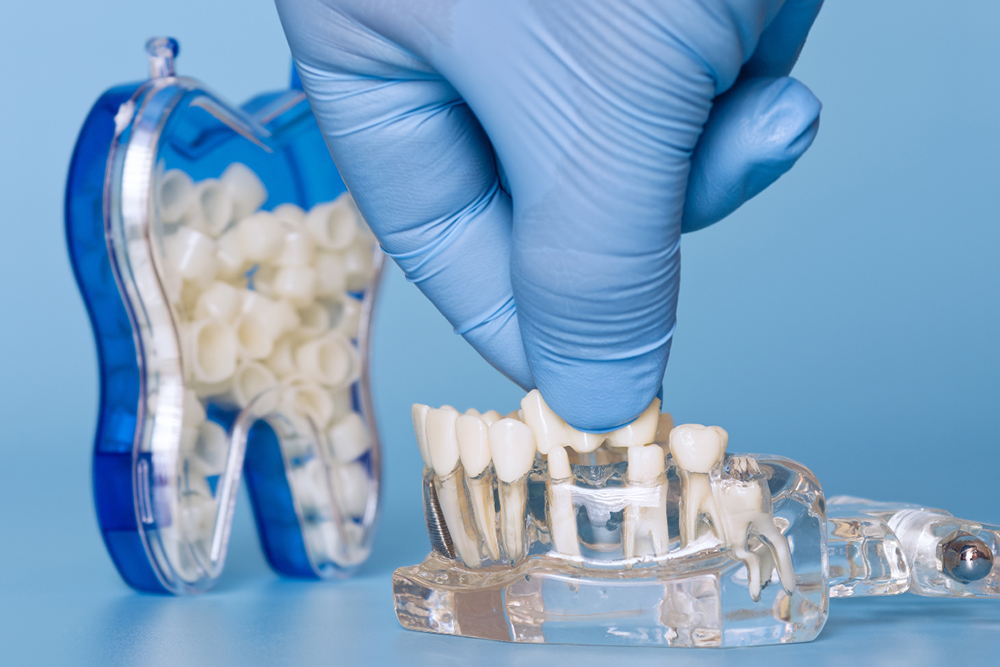
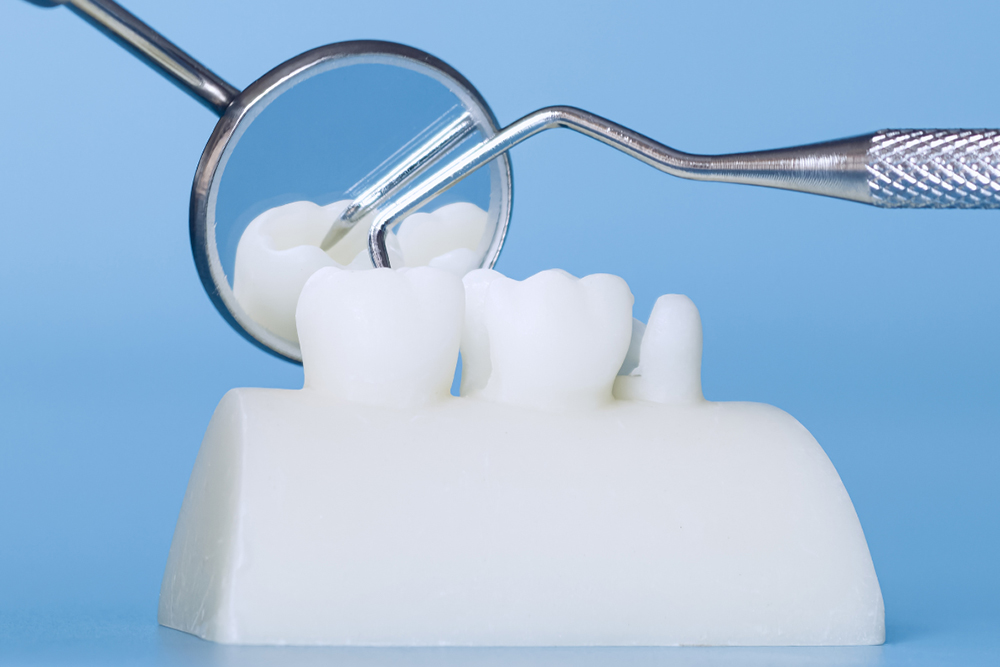
Losing a tooth or facing severe tooth damage requires important decisions about restoration options. At St. Jacobs Dental Care, patients often ask about the differences between dental crowns & bridges and dental implants. Both treatments effectively restore function and appearance, but they work in fundamentally different ways. Understanding the clinical factors, success rates, and long-term costs helps patients make informed choices about their dental health. The right solution depends on your unique situation, oral health status, and personal preferences.
Clinical Factors That Determine the Best Treatment
Several important factors influence whether dental crowns & bridges or implants are the better choice for your situation.
Bone Health and Density
Dental implants require adequate jawbone to support the titanium post. If you've been missing teeth for an extended period, bone loss may have occurred. This can make implant placement challenging or require bone grafting first.
Dental crowns & bridges don't require specific bone density levels. Crowns restore damaged teeth using the existing tooth root. Bridges rely on adjacent teeth for support rather than the jawbone.
Adjacent Tooth Condition
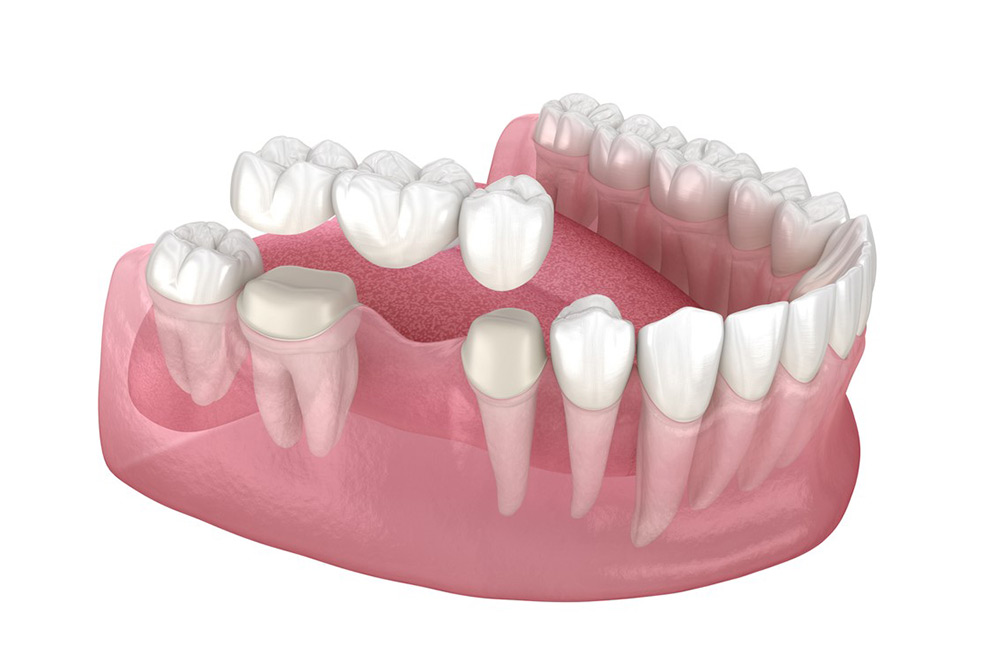
The health of neighboring teeth plays a crucial role in treatment selection. Bridges require preparing the teeth on either side of the gap. These teeth are shaped to support crowns that hold the bridge in place.
If adjacent teeth are healthy and unrestored, some patients prefer implants to avoid altering these teeth. However, if neighboring teeth already have large fillings or need crowns anyway, a bridge can address multiple issues simultaneously.
Number of Missing Teeth
The number and location of missing teeth affects treatment planning. A single missing tooth can be replaced with either an implant or a bridge. Multiple missing teeth in a row might be better suited to a bridge or implant-supported bridge.
Medical Considerations
Certain health conditions affect treatment options. Uncontrolled diabetes, active gum disease, or immune system disorders can complicate implant healing. Heavy smoking also reduces implant success rates.
Dental crowns & bridges typically have fewer medical contraindications. They represent a viable option for patients who aren't good implant candidates due to health factors.
Timeline Requirements
Implants require several months from start to finish. The titanium post must integrate with bone before receiving the final crown. This process, called osseointegration, typically takes three to six months.
Dental crowns & bridges can be completed much faster. Most cases require just two to three appointments over several weeks. For patients needing quick restoration, this timeline advantage is significant.
Success Rates and Maintenance for Dental Crowns and Bridges
Understanding long-term outcomes helps patients set realistic expectations for their chosen treatment.
Success Rates for Dental Crowns and Bridges
Dental crowns have excellent success rates when properly maintained. Studies show that crowns typically last 10 to 15 years or longer. Some crowns remain functional for 20 to 30 years with excellent care.
Bridges also demonstrate strong success rates. Traditional bridges typically last 10 to 15 years. The longevity depends on the health of supporting teeth and the patient's oral hygiene habits.
At St. Jacobs Dental Care, located at 10 Parkside Dr in St. Jacobs, the team uses high-quality materials and precise techniques. This attention to detail maximizes the lifespan of dental crowns & bridges.
Maintenance Requirements
Dental crowns and bridges require diligent oral hygiene to ensure longevity. Daily brushing and flossing remain essential. Special floss threaders or water flossers help clean under bridges where regular floss cannot reach.
Regular dental check-ups every six months allow for monitoring of restorations. The dentist checks for signs of wear, decay around margins, or issues with supporting teeth.
Patients should avoid habits that stress restorations, including:
- Chewing ice or hard candies
- Using teeth as tools to open packages
- Grinding or clenching teeth (a night guard may be recommended)
- Biting directly into very hard foods
Potential Complications
While dental crowns & bridges are highly successful, potential issues can occur. Decay can develop at the margin where the crown meets natural tooth. This is why excellent oral hygiene is crucial.
The supporting teeth for bridges bear additional chewing forces. Over time, this can lead to increased wear or stress. Regular monitoring helps identify problems early.
Success Rates and Maintenance for Dental Implants
Dental implants have become increasingly popular due to their high success rates and natural feel.
Implant Success Statistics
Modern dental implants boast success rates exceeding 95 percent. With proper care, many implants last a lifetime. The titanium post integrates permanently with jawbone, creating a stable foundation.
Implant Maintenance Needs
Implants require similar daily care to natural teeth. Brushing twice daily and flossing remain essential. Special attention to the gum tissue around implants helps prevent peri-implantitis (inflammation around implants).
Regular professional cleanings and examinations ensure implant health. The dentist monitors bone levels and checks for any signs of complications.
Implant Considerations
While implants don't decay like natural teeth, the surrounding gum and bone tissue require healthy maintenance. Poor oral hygiene can lead to implant failure. Smoking significantly increases the risk of implant complications.
Cost Analysis: Dental Crowns & Bridges vs Implants
Financial considerations play an important role in treatment decisions. Understanding both initial and long-term costs provides a complete picture.
Initial Investment Comparison
Dental crowns & bridges typically require lower upfront investment compared to implants. A single crown or three-unit bridge costs less than an implant with crown. The procedures are also less complex and don't involve surgical components.
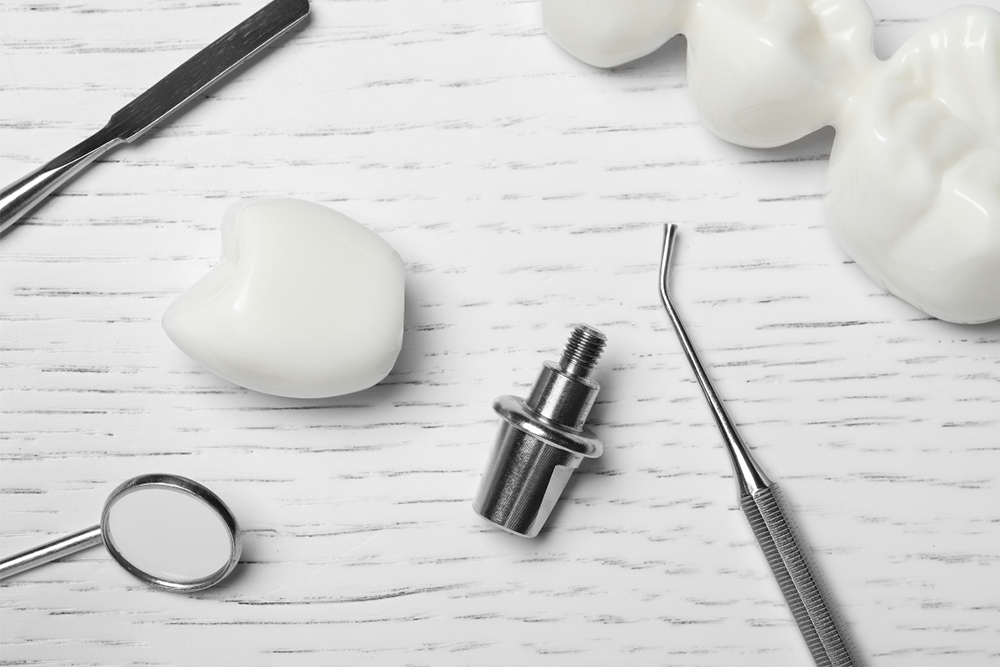
Dental implants require higher initial investment. The cost includes the surgical placement, the implant post, the abutment (connector piece), and the final crown. If bone grafting is needed, this adds to the expense.
Insurance Coverage Differences
Many dental insurance plans provide better coverage for dental crowns & bridges compared to implants. Traditional restorations are often considered standard care with higher reimbursement percentages.
Implant coverage varies widely by insurance plan. Some plans offer partial coverage, while others consider implants cosmetic and provide no benefits.
Lifetime Cost Considerations
While implants cost more initially, they may offer better long-term value. Implants can last a lifetime, potentially eliminating replacement costs. They also don't affect adjacent teeth, avoiding future complications with neighboring teeth.
Dental crowns & bridges typically need replacement every 10 to 15 years. This means additional costs over a lifetime. Bridges also place stress on supporting teeth, which may eventually need their own treatment.
Value Beyond Cost
Cost represents just one factor in treatment decisions. The value of restored function, improved confidence, and quality of life should also be considered. Both dental crowns & bridges and implants successfully restore these important aspects.
Making Your Decision at St. Jacobs Dental Care
Choosing between dental crowns & bridges and implants requires careful consideration of multiple factors. The team at St. Jacobs Dental Care provides comprehensive consultations to help patients understand their options.
During your consultation, the dentist will:
- Evaluate your oral health and bone density
- Discuss your medical history and any relevant conditions
- Review your timeline and scheduling preferences
- Explain treatment options specific to your situation
- Provide detailed cost estimates and insurance information
- Answer all your questions about procedures and outcomes
Ready to explore your options for dental crowns & bridges or implants? Contact St. Jacobs Dental Care at 519-664-2434 or email info@stjacobsdentalcare.ca to schedule your consultation. The office is conveniently located at 10 Parkside Dr in St. Jacobs, with appointments available Monday through Thursday from 8:00 AM to 5:00 PM and Friday mornings from 8:00 AM to 12:00 PM.
Whether you choose dental crowns & bridges or implants, professional restoration can transform your smile and restore full function for years to come.
Cosmetic Dentistry in St. Jacobs: Teeth Whitening
January 22, 2026 / DENTISTRY
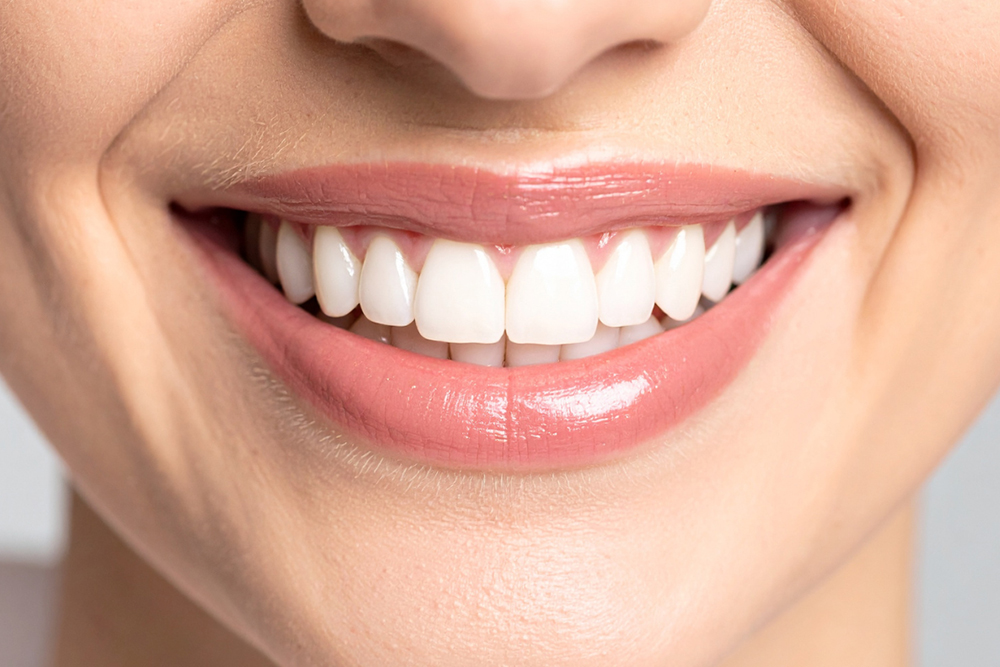

A bright, white smile can boost confidence and make a lasting impression in both personal and professional settings. At St. Jacobs Dental Care, professional teeth whitening represents one of the most popular cosmetic dentistry in St. Jacobs services requested by patients. Understanding the difference between professional whitening and over-the-counter options helps patients make informed decisions about achieving their brightest smile. Professional treatments offer superior results, safety, and customization that drugstore products simply cannot match.
In-Office Whitening: Cosmetic Dentistry in St. Jacobs
Fast, professional whitening with immediate results
Professional in-office whitening delivers the most dramatic results in the shortest amount of time. This approach to cosmetic dentistry in St. Jacobs is ideal for patients who want immediate improvements for special occasions or simply prefer the convenience of single-visit treatment.
How In-Office Whitening Works
Professional whitening systems use higher concentrations of bleaching agents than over-the-counter products. These powerful formulations are safe when applied by trained dental professionals who take precautions to protect gums and soft tissues.
- Thorough cleaning to remove surface stains and debris
- Application of protective barriers to gums and lips
- Careful placement of professional-strength whitening gel on teeth
- Activation with specialized light or laser technology (in some systems)
- Multiple application cycles during a single appointment
- Post-treatment fluoride application to reduce sensitivity
Results You Can See Immediately
One of the biggest advantages of in-office whitening is the immediate transformation. Patients often see their teeth lighten by several shades in just one appointment. This makes in-office whitening perfect for upcoming weddings, job interviews, or other important events.
At St. Jacobs Dental Care, located at 10 Parkside Dr in St. Jacobs, the dental team carefully monitors the whitening process. This ensures optimal results while minimizing any potential sensitivity or discomfort.
Who Benefits Most from In-Office Whitening
In-office whitening works best for patients with:
- Healthy teeth and gums free from decay or disease
- Yellow or brown tooth discoloration (rather than gray tones)
- Time constraints requiring fast results
- Preference for professional supervision throughout treatment
- Desire for maximum whitening in minimum time
Custom Take-Home Whitening Trays
Professional results with at-home convenience
Take-home whitening trays represent another excellent option in cosmetic dentistry in St. Jacobs. This approach offers professional-quality results with the convenience of whitening on your own schedule.
Professional vs. Drugstore Trays
While drugstore whitening kits are readily available, they cannot compare to custom trays from your dentist. Professional take-home whitening offers several key advantages:
- Custom-fitted trays that match your teeth precisely
- Professional-grade whitening gel with optimal concentration
- Even distribution of whitening agent across all tooth surfaces
- Reduced risk of gel leaking onto gums
- Better contact between gel and teeth for superior results
- Professional guidance on usage and timing
The Custom Tray Process
Creating custom whitening trays involves taking precise impressions of your teeth. These impressions are used to fabricate trays that fit your mouth perfectly. The snug fit ensures the whitening gel stays in contact with your teeth while protecting your gums.
- How much gel to use in each tray
- How long to wear trays each day
- Whether to whiten during the day or overnight
- How to clean and store trays properly
- When to expect visible results
Gradual, Controlled Whitening
Take-home whitening typically produces results over one to two weeks. This gradual approach allows for controlled lightening and often results in less sensitivity compared to in-office treatments. Patients can also adjust their whitening schedule based on their sensitivity levels and desired results.
Comparing Professional Cosmetic Dentistry in St. Jacobs Options
Choosing the right whitening method for your needs
Both in-office and take-home whitening have distinct advantages. Understanding these differences helps patients choose the best option for their needs.
Speed of Results
In-office whitening delivers immediate results in a single appointment. Take-home trays require consistent use over several days or weeks. For time-sensitive situations, in-office whitening is the clear choice.
Convenience and Control
Take-home trays offer flexibility to whiten on your schedule. You control when and where you whiten. In-office treatments require scheduling an appointment but eliminate the need for daily home application.
Sensitivity Management
Both methods can cause temporary sensitivity. Take-home whitening allows you to adjust treatment frequency if sensitivity occurs. In-office treatments are completed in one session, so sensitivity is typically short-lived.
Cost Considerations
In-office whitening typically costs more upfront but delivers faster results. Take-home trays represent a more budget-friendly option while still providing professional-quality whitening. At St. Jacobs Dental Care, the team can discuss both options and help you choose based on your budget and goals.
Maintenance Protocols for Long-Lasting Results
Protecting your brighter smile
Achieving a bright smile is just the first step. Maintaining your whitening results requires ongoing care and occasional touch-ups.
Daily Habits for Whiter Teeth
Protecting your investment in cosmetic dentistry in St. Jacobs means adopting habits that prevent new stains:
- Brush twice daily with whitening toothpaste
- Floss daily to remove plaque between teeth
- Rinse after consuming staining foods or beverages
- Use a straw for coffee, tea, and red wine
- Avoid tobacco products that cause severe staining
- Attend regular dental cleanings every six months
Touch-Up Schedules
Even with excellent care, teeth naturally darken over time. Most patients benefit from periodic touch-ups to maintain their bright smile. The frequency depends on individual factors like diet, oral hygiene, and lifestyle habits.
- Every 6–12 months for most patients
- More frequently for coffee or wine enthusiasts
- Less often for those who avoid staining substances
- As needed before special events or occasions
Patients with custom take-home trays can easily perform touch-ups at home. A few nights of whitening can refresh your smile and maintain your results.
Why Choose Professional Whitening – Cosmetic Dentistry in St. Jacobs
Clear advantages over over-the-counter products
Over-the-counter whitening products flood the market, but professional cosmetic dentistry in St. Jacobs offers significant advantages.
Safety and Supervision
Professional whitening occurs under dental supervision. The team at St. Jacobs Dental Care evaluates your oral health before whitening. This ensures you're a good candidate and identifies any issues that need addressing first.
Superior Results
Professional whitening systems use higher-quality ingredients and deliver more dramatic, longer-lasting results. Custom trays ensure even whitening across all visible tooth surfaces.
Customized Treatment
Your dentist can adjust whitening protocols based on your specific needs, sensitivity levels, and desired outcomes. This personalization is impossible with one-size-fits-all drugstore products.
Start Your Whitening Journey with Cosmetic Dentistry in St. Jacobs
Ready to achieve the bright, confident smile you deserve through cosmetic dentistry in St. Jacobs? Contact St. Jacobs Dental Care at 519-664-2434 or email info@stjacobsdentalcare.ca to schedule your whitening consultation. The office is conveniently located at 10 Parkside Dr in St. Jacobs, with appointments available Monday through Thursday from 8:00 AM to 5:00 PM and Friday mornings from 8:00 AM to 12:00 PM.
Whether you choose in-office whitening for immediate results or custom take-home trays for gradual lightening, professional cosmetic dentistry in St. Jacobs delivers the safe, effective whitening you're looking for.
Archive